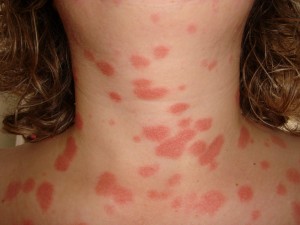
Chickenpox is a common contagious disease that mainly affects children. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which spreads easily from one person to another through coughing, sneezing, or direct contact with the fluid from chickenpox blisters. The disease usually begins with mild symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and headache, followed by a red, itchy rash that turns into small fluid-filled blisters. Although chickenpox is often considered a mild childhood illness, it can sometimes lead to complications, especially in young infants or people with weak immune systems.
When a child becomes infected with chickenpox, the body’s immune system reacts by fighting the virus. After recovery, the immune system remembers the virus and can protect the body if it encounters it again in the future. This process is sometimes referred to as natural vaccination, because the body develops immunity naturally after being exposed to the disease. For many children, this natural immunity lasts for life, making reinfection very rare.
Images of a sick boy with chickenpox holding a toy bear often reflect the emotional and human side of the illness. A child suffering from chickenpox may feel uncomfortable, tired, and anxious due to the itching and fever. A familiar object, such as a favorite toy, can provide comfort and emotional support during this difficult time. This highlights the importance of care, love, and reassurance in addition to medical treatment when a child is ill.
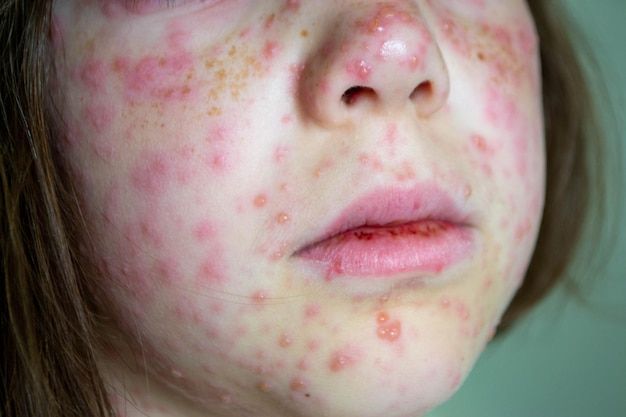
Despite the fact that natural immunity can develop after infection, relying on natural vaccination is not always safe. Chickenpox can sometimes cause serious complications such as skin infections, pneumonia, or inflammation of the brain. For this reason, modern medicine strongly recommends vaccination against chickenpox. The chickenpox vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect children from the disease and to reduce the spread of the virus in the community.
Vaccination not only protects the individual child but also helps protect others, including newborn babies and people with weakened immune systems who may not be able to receive the vaccine themselves. By reducing the number of infected people, vaccination plays a key role in public health and disease prevention.
In conclusion, chickenpox is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella virus, and while natural infection can lead to long-lasting immunity, it also carries potential risks. Medical vaccination remains the safest and most reliable way to prevent the disease. Alongside medical care, emotional support and proper attention are essential to help sick children recover comfortably and safely. Promoting awareness, hygiene, and vaccination is crucial for maintaining a healthy society.